INTELLIGENCE MANAGEMENT
Intelligence Management - The basics - Lesson 1
Intelligence Management - Structures - Lesson 2
Intelligence Management - The basics
Let's keep this simple:
We collect information.
We process that information and create intelligence.
This process will create different types of intelligence product.
We use these intelligence products in support our the agency's mandate.
Information can be collected in many different ways for example: open source, human sources (confidential informants), crime stoppers, surveillance, intercepting communications (wire taps) and listening devices.
When collected the information should always be submitted to a central intelligence unit, within the agency, where properly trained intelligence staff can process it. The processing will include evaluation of the information, including both the provenance and the content, and the integration with existing intelligence.
As a result of this processing the intelligence staff create intelligence products, for example: intelligence reports, threat assessments, risk assessments, problem profiles, social network analysis etc.
Every entity (a person place or thing) contained in an intelligence product is given a unique reference number that identifies it from every other person place and thing. These numbers stay with the entity for as long as the intelligence is retained.
The intelligence products are all stored in an intelligence repository, a centralized database where staff with predefined access can view the content at any time.
The central intelligence unit disseminates relevant intelligence products to identified customers.
Customers use those products to further their objectives and send the results back to the central intelligence unit along with any other information they have obtained.
For a comprehensive explanation of this see our publication: Managing Intelligence: A Guide for Law Enforcement Professionals
______________________________________________________________________
Lesson 2: Intelligence Management - Structures
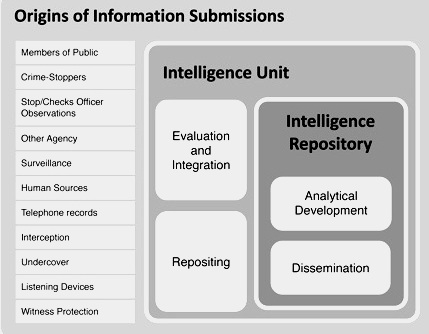
If we want to manage intelligence effectively in line with the concepts of intelligence led policing we need a structure within our agency that is both simple and effective. The model below illustrates in intelligence management structure. There are a number of core principles that accompany this structure:
All information that is to be used for intelligence purposes obtained is submitted to a central intelligence unit - the ‘Intelligence Unit’. No information can be used for warrants/investigations etc. until it has gone through the Intelligence Unit. This eliminates risks including corruption and the compromise of investigations.
The Intelligence unit processes that information, grades the reliability of the source and the credibility of each piece of information and then lodges a numbered intelligence report in a central intelligence repository. The Intelligence Unit also disseminates that intelligence to identified customers, internally and externally.
Members of that agency can access the repository based on their allotted task and clearance level.
Other analytical products can be created using these intelligence reports and other information. These are also lodged in the central intelligence repository.
IF this is done all intelligence is graded and managed to an identified set of standards. Disclosure is dealt with effectively and the risk that officers make up informants or information is greatly reduced. You will have a much clearer intelligence led picture.
If you want to learn more contact us at info@hsmtraining.com or have a read at Managing Intelligence - A Guide for Law Enforcement Professionals.